What is Infertility?
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive a child after one year or more of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. Many couples end up confused between multiple infertility treatments. Let us throw some light on it in detail. It is a condition that affects both men and women equally and is a significant concern for many couples worldwide. It’s important to understand that infertility is a medical condition, not a reflection of personal inadequacy or failure.
There are two main types of infertility:
Primary Infertility: This refers to couples who have never been able to conceive a child despite having regular unprotected intercourse for at least one year.
Secondary Infertility: This refers to couples who have conceived at least once in the past but are now unable to achieve another pregnancy.
Infertility is more common than many people realize, affecting approximately one in six couples globally. There are fertility treatments available that can complete your dream of parenthood.
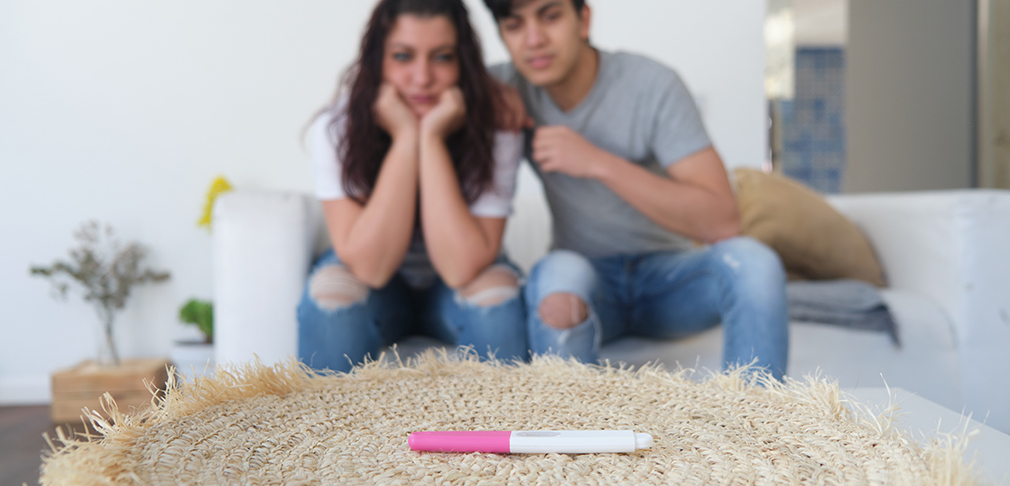

What are the causes of Infertility ?
The causes of infertility are diverse and can originate from either the male or female partner, or a combination of factors. In some cases, the cause of infertility remains unexplained even after thorough medical evaluation.
Causes of Female Infertility:
Ovulation Disorders: These are common and involve infrequent, irregular, or absent ovulation. Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), hypothalamic dysfunction, premature ovarian insufficiency (POI), and hyperprolactinemia can disrupt normal ovulation.
Fallopian Tube Damage or Blockage (Tubal Infertility): with reference to the female reproductive system. Blocked or scarred fallopian tubes can prevent the egg from traveling to the uterus and the sperm from reaching the egg. This can be caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, or previous surgeries.
Uterine Issues: Abnormalities in the uterus, such as fibroids, polyps, congenital uterine malformations, or adhesions (scar tissue), can interfere with embryo implantation or increase the risk of miscarriage.
Endometriosis: This condition involves the growth of uterine-like tissue outside the uterus, which can affect the function of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus.
Cervical Factors: Problems with the cervix, including cervical stenosis or the inability to produce mucus that facilitates sperm transport, can contribute to infertility.
Age-Related Factors: A woman's fertility naturally declines with age, particularly after the mid-30s, due to a decrease in the number and quality of eggs.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, being underweight, and extreme exercise can negatively affect ovulation and overall fertility. Small changes in your daily lifestyle can influence female fertility treatment.
Causes of Male Infertility:
Sperm Disorders: These are the most common causes of male infertility and include:
- Low Sperm Count (Oligospermia): Having fewer sperm than normal.
- Absent Sperm (Azoospermia): Complete lack of sperm in the ejaculate.
- Poor Sperm Motility (Asthenozoospermia): Sperm that do not swim effectively.
- Abnormal Sperm Morphology (Teratozoospermia): Sperm with an abnormal shape.
Testicular Issues: with reference to the male reproductive system, Conditions affecting the testicles, such as varicocele (swollen veins in the scrotum), infections, undescended testicles, or testicular injury, can impair sperm production.
Ejaculation Disorders: Problems like retrograde ejaculation (sperm going into the bladder instead of out the penis) or premature ejaculation can hinder fertilization.
Obstruction: Blockages in the tubes that carry sperm (epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts) can prevent sperm from being released in the ejaculate.
Hormonal Imbalances: Abnormal levels of hormones produced by the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, or testicles can affect sperm production.
Genetic Factors: Certain genetic conditions, such as cystic fibrosis or Klinefelter syndrome, can cause male infertility.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, obesity, and exposure to toxins can negatively impact sperm quality and production. It plays an important role in male fertility treatment.
Why is Addressing Infertility Important?
Addressing infertility is crucial for several significant reasons that extend beyond the desire to have children:
Reproductive Health and Well-being: Infertility is a disease of the reproductive system and can have significant physical and psychological impacts on individuals and couples. Addressing it is an integral part of overall reproductive healthcare.
Emotional and Psychological Impact: The inability to conceive can lead to considerable emotional distress, including feelings of sadness, anger, frustration, guilt, inadequacy, anxiety, and depression. Addressing infertility provides access to emotional support, counseling, and potential solutions that can alleviate this burden.
Relationship Strain: Infertility can put a significant strain on a couple's relationship. Open communication, shared understanding, and seeking solutions together can strengthen their bond, regardless of the outcome.
Achieving Family-Building Goals: For many individuals and couples, having children is a deeply cherished life goal. Addressing infertility offers the possibility of achieving this dream through various treatment options.
Making Informed Decisions: Understanding the causes of infertility and the available treatment options empowers individuals and couples to make informed decisions about their reproductive future. This includes exploring different treatment paths, considering adoption, or choosing to remain childfree.
Social and Cultural Factors: In many societies, there is significant social and cultural pressure to have children. Infertility can lead to social stigma, isolation, and feelings of being different. Addressing it can help individuals navigate these social challenges and find support.
Economic Impact: The costs associated with infertility diagnosis and treatment can be substantial. Advocating for better access to affordable care and insurance coverage is an important aspect of addressing infertility on a broader scale.
Preventing Further Complications: In some cases, the underlying causes of infertility may be linked to other health issues that require medical attention. Addressing infertility can lead to the diagnosis and management of these conditions.
In essence, addressing infertility is about providing comprehensive care that encompasses the physical, emotional, psychological, and social well-being of individuals and couples facing challenges in building their families. It’s about offering hope, support, and informed choices.
What are the Different Types of Fertility Treatments?
A range of fertility treatments are available to help individuals and couples overcome infertility. The specific treatment recommended depends on the underlying cause of infertility, the age of the individuals involved, the duration of infertility, and personal preferences. These treatments can be broadly categorized as:
Fertility Medications: These are often the first line of treatment, particularly for ovulation disorders. Medications can stimulate or regulate ovulation in women and improve sperm production or function in men.
Surgical Procedures: Surgery may be necessary to correct structural problems that contribute to infertility. In women, this can include procedures to repair blocked fallopian tubes, remove fibroids or polyps, or treat endometriosis. In men, surgery may be performed to correct varicoceles or blockages in the reproductive tract, or to retrieve sperm directly.
Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART): ART involves medical procedures where eggs and sperm are handled outside the body. The most common ART technique is In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). Other ART procedures include:
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Washed and concentrated sperm are placed directly into the woman's uterus around the time of ovulation. This is often used for mild male factor infertility, unexplained infertility, or when using donor sperm.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into an egg in a lab dish. This is often used in cases of severe male factor infertility or previous IVF fertilization failures.
- Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT): Eggs are retrieved from the woman's ovaries and mixed with sperm before being directly placed into the fallopian tubes. Fertilization occurs inside the woman's body.
- Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT): Eggs are fertilized with sperm in a lab, and the resulting zygotes (fertilized eggs) are then transferred to the fallopian tubes.
- Donor Eggs, Sperm, or Embryos: These options are considered when one or both partners have issues with their gametes or when there is a genetic risk.
- Gestational Carrier (Surrogacy): Another woman carries and delivers a baby for a couple who cannot conceive or carry a pregnancy themselves. The gestational carrier has no genetic link to the baby.
Lifestyle Modifications and Complementary Therapies: While not medical treatments in themselves, adopting a healthy lifestyle (maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol and caffeine intake, managing stress) can improve fertility. Some individuals also explore complementary therapies like acupuncture or herbal remedies, although their effectiveness is often not scientifically proven. Small habit influence the output of fertility treatments.
Two of the Most Common Fertility Treatments Are:
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): As mentioned above, IUI treatment involves placing washed and concentrated sperm directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation. This procedure aims to increase the number of sperm that reach the egg, thereby improving the chances of fertilization. IUI is often recommended for couples with mild male factor infertility, unexplained infertility, or cervical mucus issues. It can be done with or without the use of ovulation-stimulating medications for the female partner. The success rates of IUI vary depending on the underlying cause of infertility, the woman's age, and whether fertility drugs are used.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF treatment is a more complex and widely used ART procedure. It involves several steps:
- Ovarian Stimulation: The woman takes fertility medications to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs.
- Egg Retrieval: Once the eggs are mature, they are retrieved from the ovaries using a minimally invasive procedure guided by ultrasound.
- Fertilization: The retrieved eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish. This can be done through conventional insemination (mixing eggs and sperm) or ICSI.
- Embryo Culture: The fertilized eggs (embryos) are allowed to develop in the laboratory for a few days.
- Embryo Transfer: One or more of the healthiest embryos are transferred into the woman's uterus through a thin catheter.
- Pregnancy Test: About two weeks after the embryo transfer, a pregnancy test is performed.
IVF is a highly effective treatment option for a wide range of fertility issues, including blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, endometriosis, severe male factor infertility (often with ICSI), ovulation disorders, and unexplained infertility. Success rates for IVF vary depending on factors such as the woman’s age, the quality of eggs and sperm, and the underlying cause of infertility.

Why Choose Us?

Natural Pregnancy First

Personalized Care

Affordable Treatment

Transparent and Ethical
Contact us today!
Contact Us
Mail Us: yashodaivfleads@gmail.com
Call Us 24/7: 8655442182
Call Us 24/7: 8655442182
Working Time
Monday - Sunday: 9.30am - 6.30pm