Embryo Freezing: Safeguarding Future Parenthood
Fertility preservation for cancer patients is a significant application of embryo freezing. Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can impair fertility. For individuals undergoing IVF as part of their IVF planning before cancer treatment, freezing embryos provides a chance to have biological children after recovery. Similarly, couples undergoing standard IVF may have surplus high-quality embryos after a fresh embryo transfer. Embryo storage through freezing allows these remaining embryos to be used in subsequent FET cycles, potentially avoiding the need for another full IVF cycle with ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval.
The core of embryo cryopreservation relies on a process called vitrification. Unlike slow-freezing methods that can lead to the formation of damaging ice crystals within the embryo, vitrification involves the rapid cooling of embryos in the presence of high concentrations of cryoprotective agents. This ultra-rapid freezing transforms the fluid inside the cells into a glass-like (vitrified) state, preventing ice crystal formation and significantly improving the survival rate of embryos upon thawing. The success of embryo development in the IVF process is paramount to having viable embryos for freezing. Embryos are typically monitored in the laboratory for several days after fertilization, and only those exhibiting healthy growth and development are considered suitable for cryopreservation.
The IVF process itself involves ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization in the lab, and the subsequent culture of embryos. Embryo freezing is integrated into this process, usually occurring at the blastocyst stage (around day 5 or 6 of development) when embryos have a higher implantation potential.
The frozen embryo transfer success rate is a key factor for individuals considering this option. Advancements in cryopreservation techniques, particularly vitrification, have led to comparable and, in some cases, even higher pregnancy rates with FET compared to fresh embryo transfers. FET IVF success can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, FET allows the woman’s body to recover fully from the ovarian stimulation phase of IVF, creating a more receptive uterine environment for implantation. High estrogen levels resulting from ovarian stimulation in a fresh cycle can sometimes negatively impact the uterine lining. In contrast, the hormonal preparation for a FET cycle is more controlled and aims to optimize uterine receptivity. Studies have shown that in cases where a high number of eggs are retrieved (more than 15-20), frozen vs fresh embryo transfer often yields better or equivalent success rates. Furthermore, babies born from frozen embryo transfers have been shown in some research to have a more optimal birth weight.
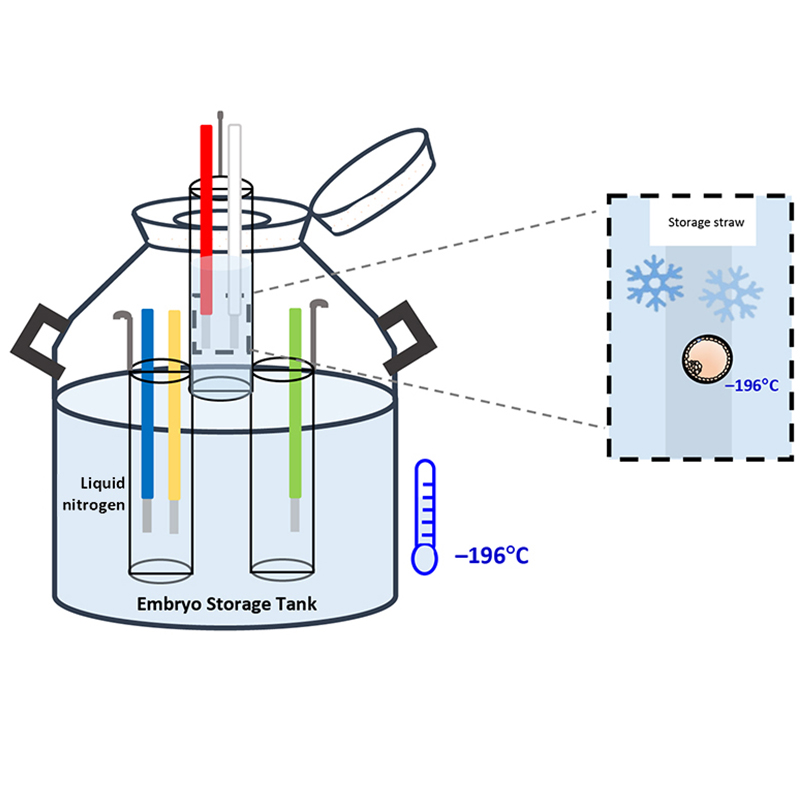
Embryo storage is a crucial aspect of embryo freezing. Once vitrified, embryos are stored in specialized tanks filled with liquid nitrogen at approximately -196 degrees Celsius. At this ultra-low temperature, all metabolic activity in the embryos ceases, allowing for long-term preservation. The question of how long embryos can be frozen has been a subject of interest. While the typical storage period is often around 10 years, successful pregnancies have been reported from embryos frozen for much longer periods, even exceeding two decades. This highlights the remarkable stability offered by cryopreservation. Safe embryo freezing practices are paramount, involving meticulous laboratory protocols, precise vitrification and thawing techniques, and stringent quality control measures to ensure the viability and safety of the stored embryos.
The embryo freezing cost in India can vary depending on the fertility clinic and the duration of storage. Generally, the initial freezing procedure and a certain period of storage are included in the cost. Subsequent annual embryo storage fees also need to be considered. While IVF treatments can be expensive, many clinics in India are striving to provide affordable fertility options, and the cost of embryo freezing is often a fraction of a full IVF cycle. Having frozen embryos can potentially make future attempts at pregnancy more cost-effective by eliminating the need for repeated ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval.
In conclusion, embryo freezing is a vital component of modern reproductive medicine. It offers hope and expands family-building options for a diverse range of individuals and couples, including those delaying childbearing, facing medical treatments that could impair fertility, or undergoing IVF. The advancements in vitrification have significantly improved the success rates of frozen embryo transfers, making it a highly effective and increasingly preferred approach in assisted reproduction. Furthermore, the long-term and safe storage of embryos provides a valuable resource for future family planning, contributing to more affordable fertility options in the long run.
Yashoda IVF Centre offers advanced embryo freezing (embryo cryopreservation) with high success rates, utilizing vitrification for safe embryo freezing. They provide comprehensive fertility preservation options within their IVF process, including expert embryo storage, contributing to potentially higher frozen embryo transfer success rates (FET IVF success) compared to fresh transfers. Consider them for reliable and ethical fertility care in India.
Embryo freezing Questions
What is embryo freezing?
How is it done?
What are the different freezing techniques?
What are the benefits of embryo freezing?
What are the risks?
Why Choose Us?




Contact us today!
Contact Us
Call Us 24/7: +1 800-123-1234
Working Time