Blastocyst Culture and Transfer: Elevating IVF Success
In the realm of Advanced IVF, Blastocyst Culture and subsequent Embryo Transfer have emerged as pivotal techniques significantly enhancing the prospects of achieving pregnancy. This sophisticated approach involves extending the in vitro culture of fertilized eggs until they reach the Blastocyst Stage, typically around day 5 or 6 of development, before transferring the most viable embryo(s) into the woman’s uterus. This strategy contrasts with earlier embryo transfers performed on day 2 or 3 after fertilization and offers several compelling advantages that contribute to improved IVF Success rates.
What is Blastocyst Culture and Embryo Transfer?
Blastocyst Culture refers to the process of growing fertilized eggs in a specialized laboratory environment for five to six days until they develop into blastocysts. A blastocyst is a more advanced stage of embryonic development characterized by a distinct cellular structure comprising an inner cell mass and an outer layer called the trophoblast. This extended culture period differs significantly from early-stage embryo transfer, where embryos are transferred on day 2 or 3, consisting of only a few cells. Waiting until Day 5 Embryo Transfer allows for a more natural selection process, as only the most robust and developmentally competent embryos are likely to reach the blastocyst stage in vitro. The benefits of waiting until Day 5 for transfer are manifold.
Why is Blastocyst Culture Important in IVF?
Blastocyst Culture plays a crucial role in optimizing IVF outcomes for several key reasons.
Firstly, it allows better embryo selection. By observing embryo development over a longer period, embryologists can identify embryos with the highest developmental competence and implantation potential. Embryos that exhibit fragmented growth or slow down in their development are less likely to implant successfully and are therefore less likely to be selected for transfer.
Secondly, transferring embryos at the blastocyst stage has a higher implantation potential. By day 5, the blastocyst has undergone significant cellular differentiation and is more synchronized with the uterine environment.
Thirdly, blastocyst transfer helps to sync with the uterine lining for better chances of pregnancy. The uterine lining, or endometrium, undergoes specific changes throughout the menstrual cycle to become receptive to embryo implantation. Transferring a blastocyst around day 5 aligns better with this window of receptivity, increasing the likelihood of successful attachment and pregnancy.
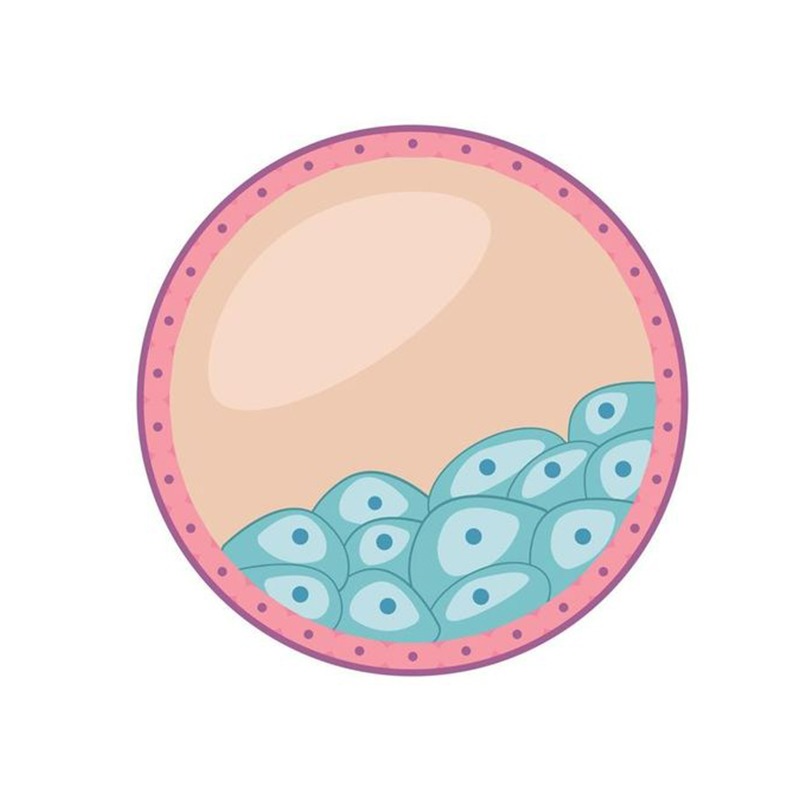
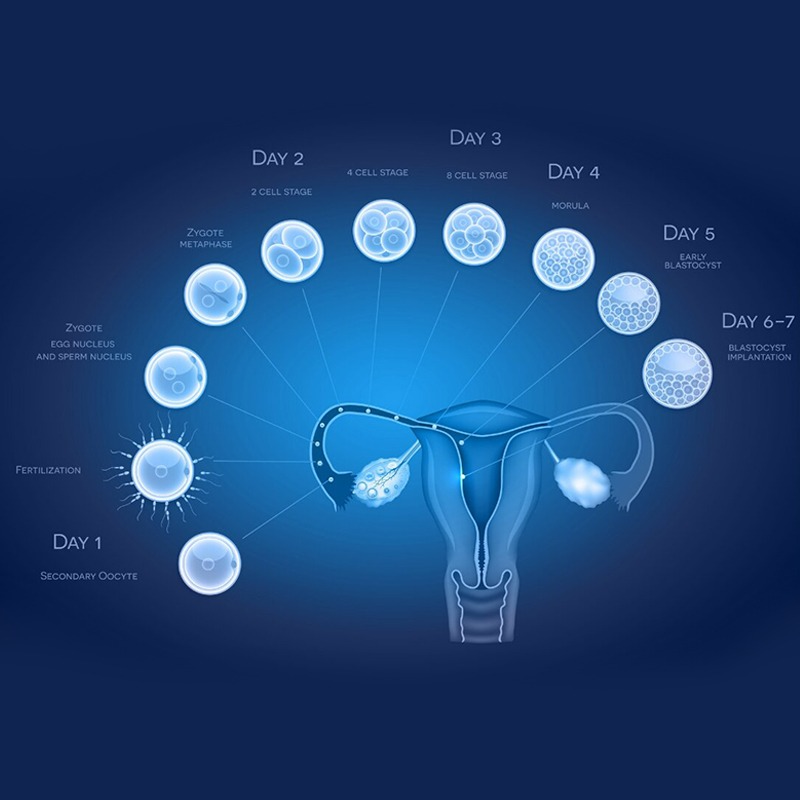
What is a Blastocyst?
Following fertilization, the zygote undergoes a series of rapid cell divisions known as cleavage. Over the next few days, these cells multiply, forming a solid ball of cells called a morula. Near day 5 or 6, the morula develops into a Blastocyst.
Key features of the Blastocyst Stage include:
The distinct structure of the blastocyst indicates a higher level of developmental competence compared to earlier-stage embryos.
Who Can Benefit from Blastocyst Transfer?
Certain patient groups may particularly benefit from Blastocyst Transfer:
Procedure of Blastocyst Culture and Transfer
The Culture process in the lab begins on day 1 with fertilized eggs (zygotes). These are carefully monitored and provided with specialized culture media that support their growth and development. Over the next five days, embryologists assess the embryos’ progression, observing their cell division, morphology, and overall quality. By day 5, the aim is to have several embryos develop into blastocysts.
The selection of the best quality blastocyst for transfer is based on morphological grading, considering factors such as the size and quality of the inner cell mass and the trophoblast, as well as the expansion of the blastocoel.
The Embryo Transfer procedure itself is a relatively simple and non-surgical process. A thin, flexible catheter is used to gently deposit the selected blastocyst(s) into the uterine cavity under ultrasound guidance. Patients are usually advised to rest for a short period after the transfer.
Success Rates of Blastocyst Transfer
Studies have consistently shown that the success rates of Day 5 vs Day 3 transfer are generally higher, particularly in patients with a good prognosis and a sufficient number of good-quality embryos. How extended culture improves implantation is attributed to the selection of more viable embryos and the improved synchronization with the receptive uterine environment. While the overall success rates depend on various factors such as the woman’s age and the quality of the embryos, blastocyst transfer has become a standard practice in many Advanced IVF clinics due to its potential to enhance pregnancy outcomes.
Advanced Embryology Techniques Involved
Several Advanced Embryology Techniques can be integrated with blastocyst culture and transfer to further optimize success:
Supporting Treatments & Medications
To further enhance the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy after blastocyst transfer, several Supporting Treatments & Medications are typically employed:
Yashoda IVF Centre offers advanced embryo freezing (embryo cryopreservation) with high success rates, utilizing vitrification for safe embryo freezing. Their experienced team and state-of-the-art lab optimize fertility preservation within their comprehensive IVF process, aiming for excellent frozen embryo transfer success rates.
Blastocyst Culture and Transfer Treatment Questions
What is the difference between a Day 3 and Day 5 embryo transfer?
Is blastocyst transfer more successful?
Will all embryos reach blastocyst stage?
Does blastocyst transfer increase chances of twins?
Is the procedure painful or risky?
Why Choose Us?




Contact us today!
Contact Us
Call Us 24/7: +1 800-123-1234
Working Time